When it comes to evaluating the actual performance of a plant, the OEE indicator is one of the most reliable tools available. This parameter allows translating the daily operation of machines into concrete data, revealing how efficiently a plant is working compared to its potential.
Used in manufacturing and automated production systems, OEE calculation allows for precise measurement of the actual utilization of plants compared to their maximum potential, highlighting inefficiencies, waste, and areas for improvement.
Continuously applying OEE calculation logic means transforming operational data into concrete levers to optimize the production process — an advantage that becomes even more significant when this data is integrated into software for industrial piping design. Tools like ESApro indeed allow plant performance relating to design choices, thanks to a multidisciplinary environment where all technical information is centralized, shared, and updated in real-time.
In this article, we will analyze the three factors that compose it and how to calculate OEE, with a technical and applicative approach designed for those who design and manage industrial plants.
What is OEE in production
Understanding the meaning of OEE, knowing its formula, and correctly applying the calculation method is essential for engineers and production managers who want to intervene specifically on productivity. This parameter does not just provide a percentage figure: it is a practical tool for interpreting the information generated by plants, optimizing processes, and guiding technical and production choices. In the context of big data in Industry 4.0, the OEE formula assumes a central role, integrating into analysis flows to support strategies based on concrete and real-time data.
OEE, an acronym for Overall Equipment Efficiency, is an indicator used to objectively evaluate the operational performance of a machine or an entire production line. Its goal is to quantify how much of the available time is actually transformed into useful production, that is, free from waste, interruptions, or slowdowns.
Unlike other metrics, it focuses exclusively on equipment efficiency, providing a percentage figure that takes into account three fundamental aspects: availability, performance, and quality. An OEE value of 100% represents the ideal, where the plant works without stops, at maximum speed, and without producing defects.
The 3 OEE factors
To measure the efficiency of a plant with the OEE index, it is necessary to break down the planned production time and analyze three main types of loss: availability, performance, and quality. Each factor affects the final result differently, and together, they form the basis for OEE calculation.
- Availability
This first parameter compares the actual operating time of the machine with the planned production time. Any interruptions, such as sudden breakdowns, lack of materials, or changeover times, reduce the availability value. Planned downtimes are also included in the analysis if they subtract useful production time.
- Performance
Performance measures how close the production process is to its optimal speed. Slower-than-expected cycles, micro-stops, or repeated malfunctions are all elements that lower this value. It is a useful indicator for identifying inefficiencies related to wear, supply problems, or operational management
- Quality
This factor considers only the compliant pieces produced on the first attempt. Anything that requires rework or is discarded negatively affects the result. The higher the percentage of components accepted without corrective actions, the higher the quality value.
Overall Equipment Efficiency is derived from the combination of these three indicators. Understanding how it works is the first step to identifying where to act concretely and how to improve OEE with targeted interventions.
But what is a good OEE score? As mentioned earlier, a theoretical value of 100% represents ideal production: no stops, no defects, and maximum pace. In reality, an OEE of 85% is considered excellent and is often indicated as a goal for high-performance plants.
A score around 60% is common in many production environments and suggests the presence of operational margins to explore. Lower values, such as a parameter of 40%, are typical in the initial monitoring phases and can quickly improve with the systematic analysis of the main causes of inefficiency.
How to calculate OEE performance
The calculation of OEE can be approached in two ways: a more immediate one, useful for having a general overview of the industrial plant, and a more structured one, which allows for precisely identifying individual areas of inefficiency.
Both methods are based on measurable data collected directly from the production lines.
Basic OEE calculation
In the simplified method, this parameter is obtained by comparing the actual productive production time with the planned production time. In other words, it measures how much of the available time was used to produce compliant pieces, at the maximum possible speed, without interruptions.
The formula is:
OEE = (Good Pieces × Ideal Cycle Time) / Planned Production Time
This approach provides a first indication of the overall efficiency level but does not highlight the individual causes of losses. For a more detailed analysis, it is preferable to break down the index into the three fundamental factors listed above.
Analytical calculation of OEE
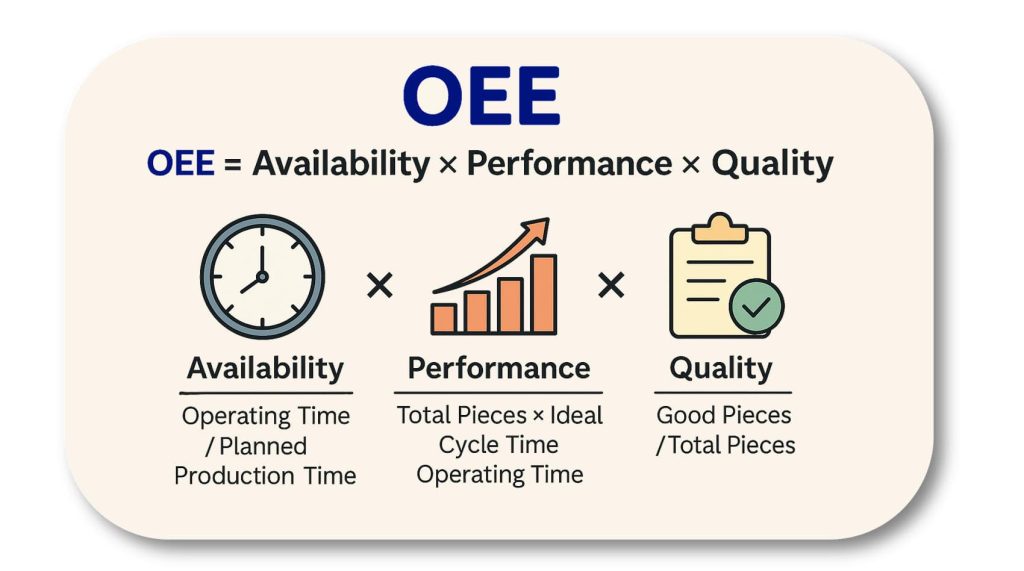
The most commonly used method for calculating OEE is based on the multiplication of three distinct coefficients: availability, performance, and quality.
Availability = Operating Time / Planned Production Time
As mentioned above, availability considers all interruptions that prevent production (such as breakdowns, lack of materials, changeovers). It is calculated by subtracting downtime from the planned time and relating the result to the planned time itself.
Performance = (Total Pieces × Ideal Cycle Time) / Operating Time
Performance measures how close the production rate is to its theoretical speed. It includes losses caused by slowdowns, micro-stops, and slower cycles than expected. If the value exceeds 100%, it is likely that the ideal cycle time was not set correctly.
Quality = Good Pieces / Total Pieces
Quality refers to the percentage of compliant products made on the first attempt. It includes scraps, rework, and any component that does not meet standards. The higher this value, the lower the losses related to quality.
Once the three factors are calculated, the parameter is obtained by multiplying them:
OEE = Availability × Performance × Quality
This approach allows for precisely identifying where losses occur and how to improve OEE in a targeted manner: by acting on machine stops, reducing cycle times, improving material quality, or optimizing the production flow. Consistently applying this formula means transforming the data collected in the plant into an operational tool for the continuous improvement of production lines.






